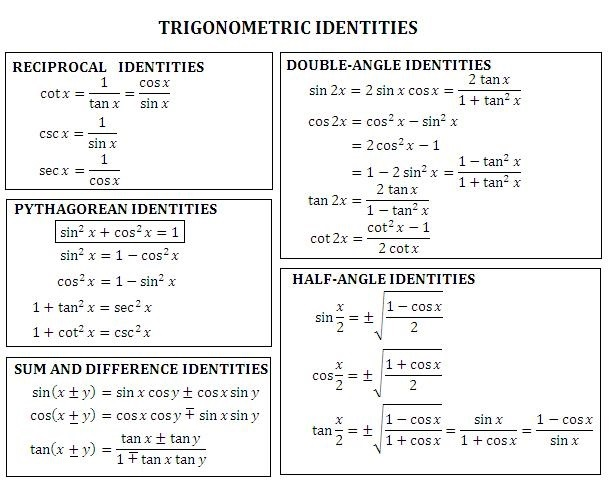
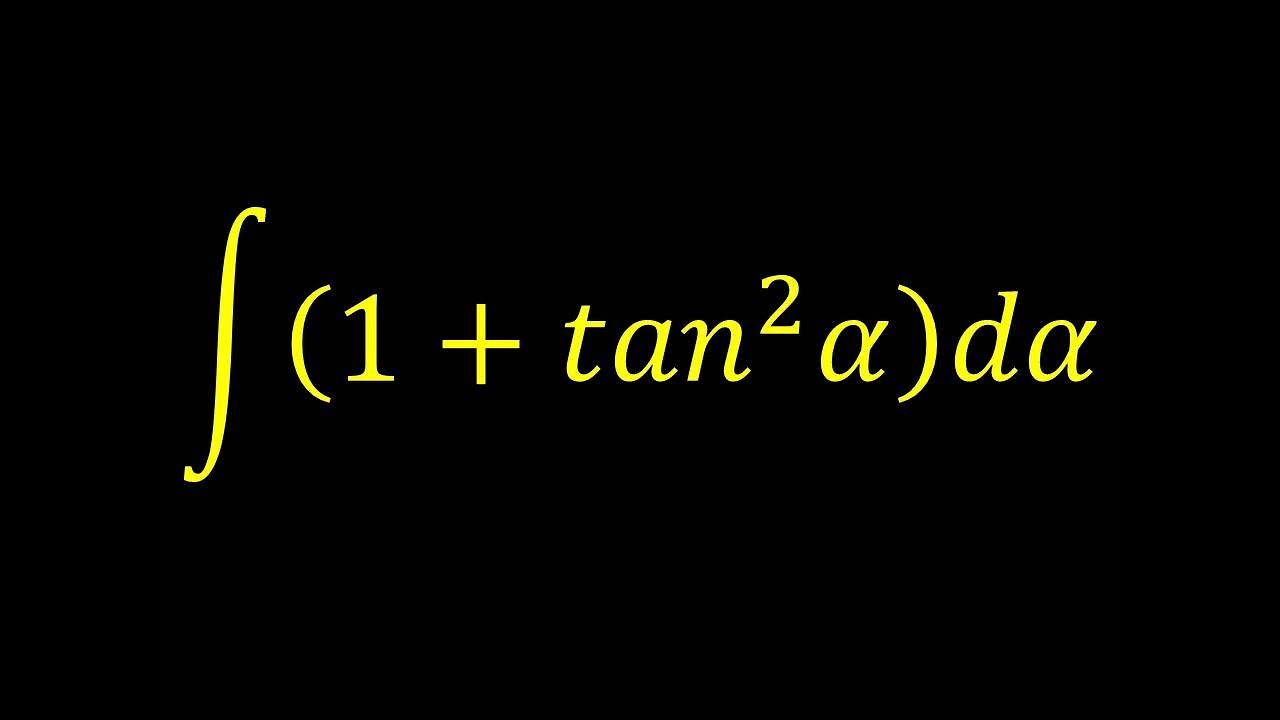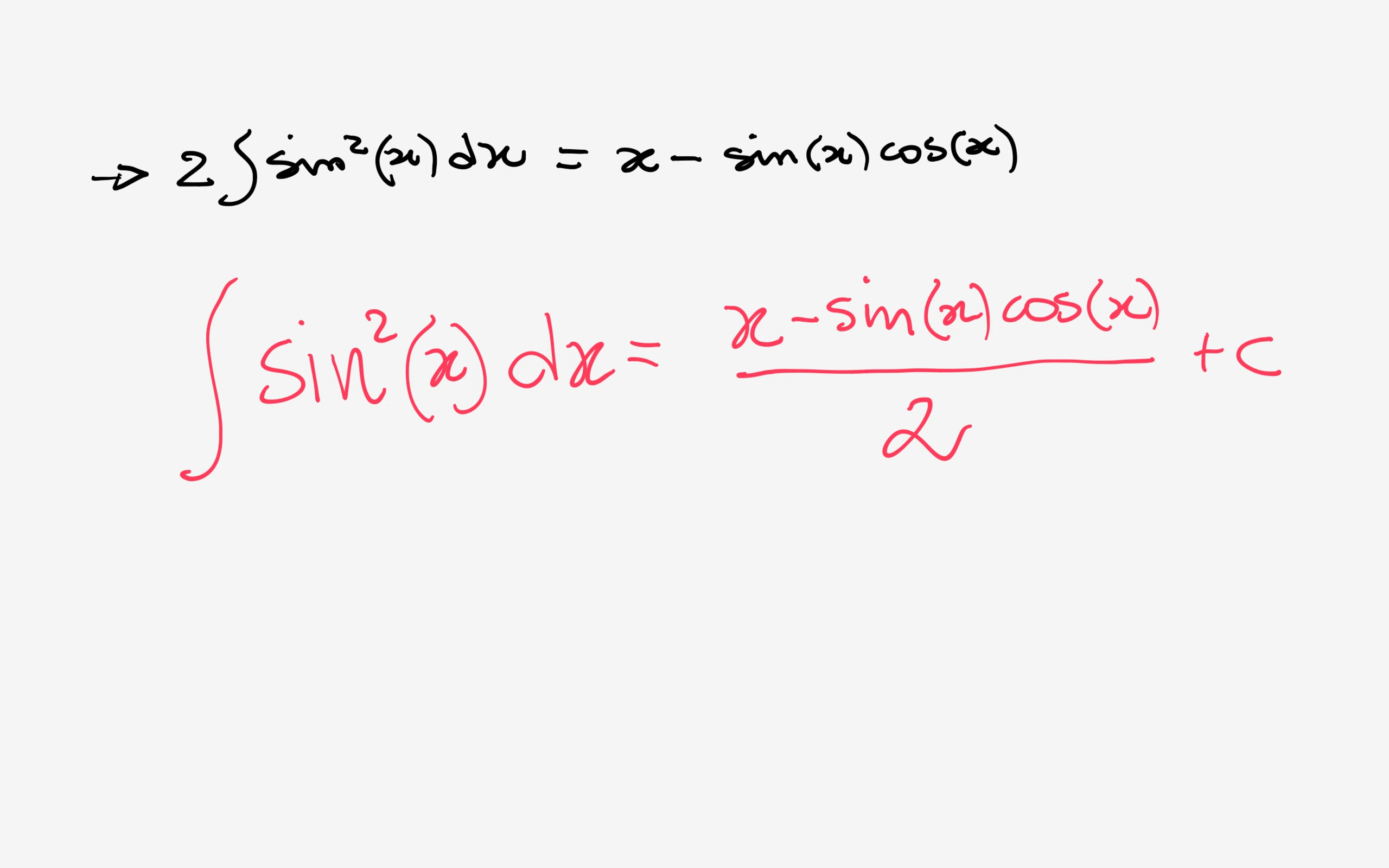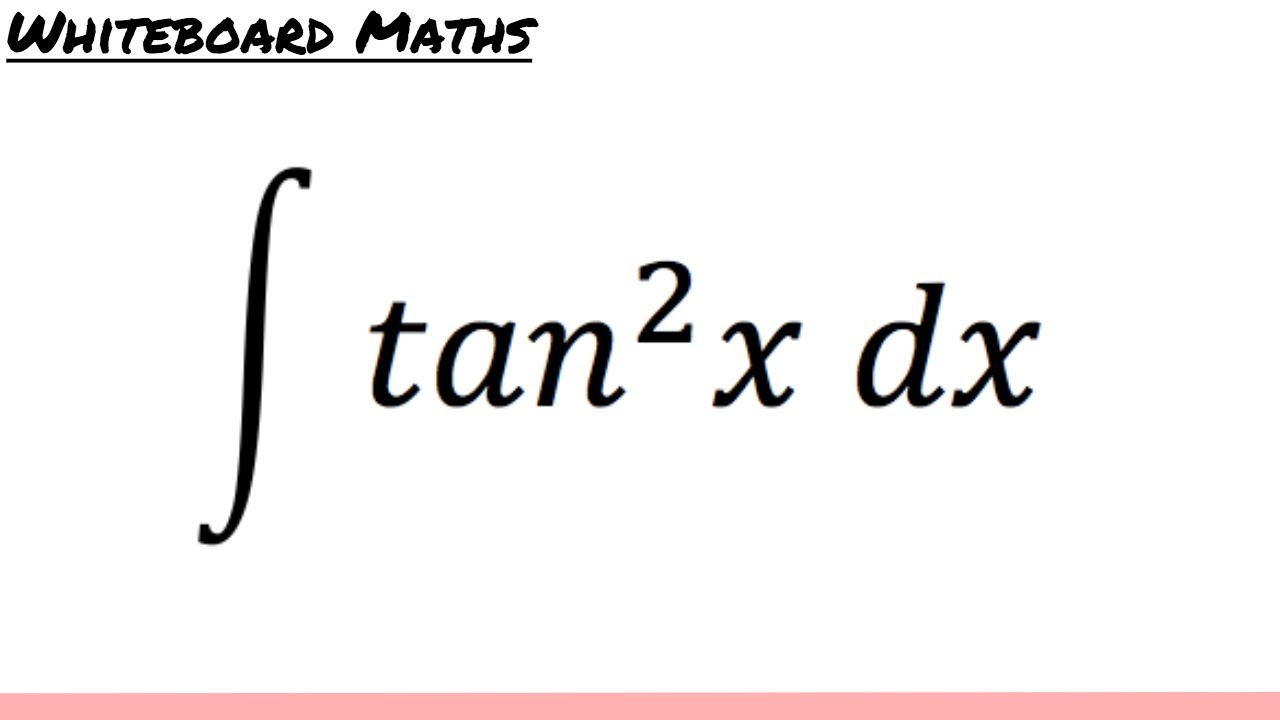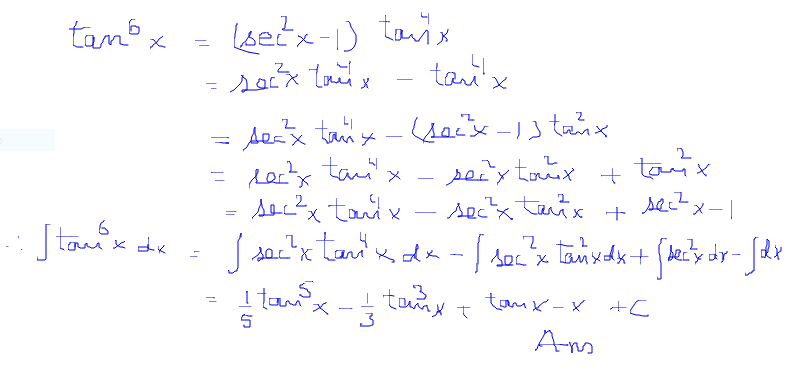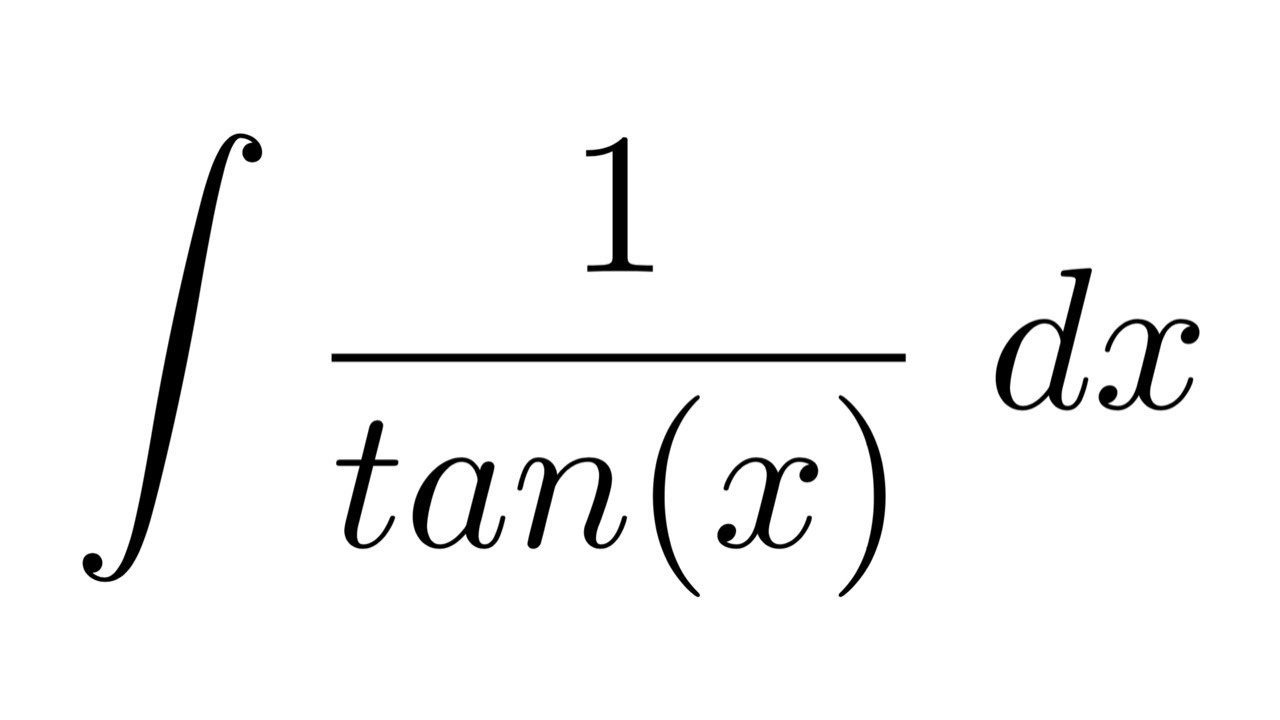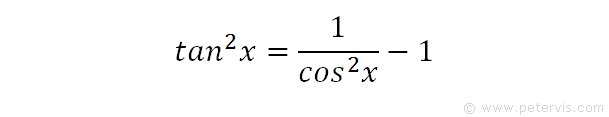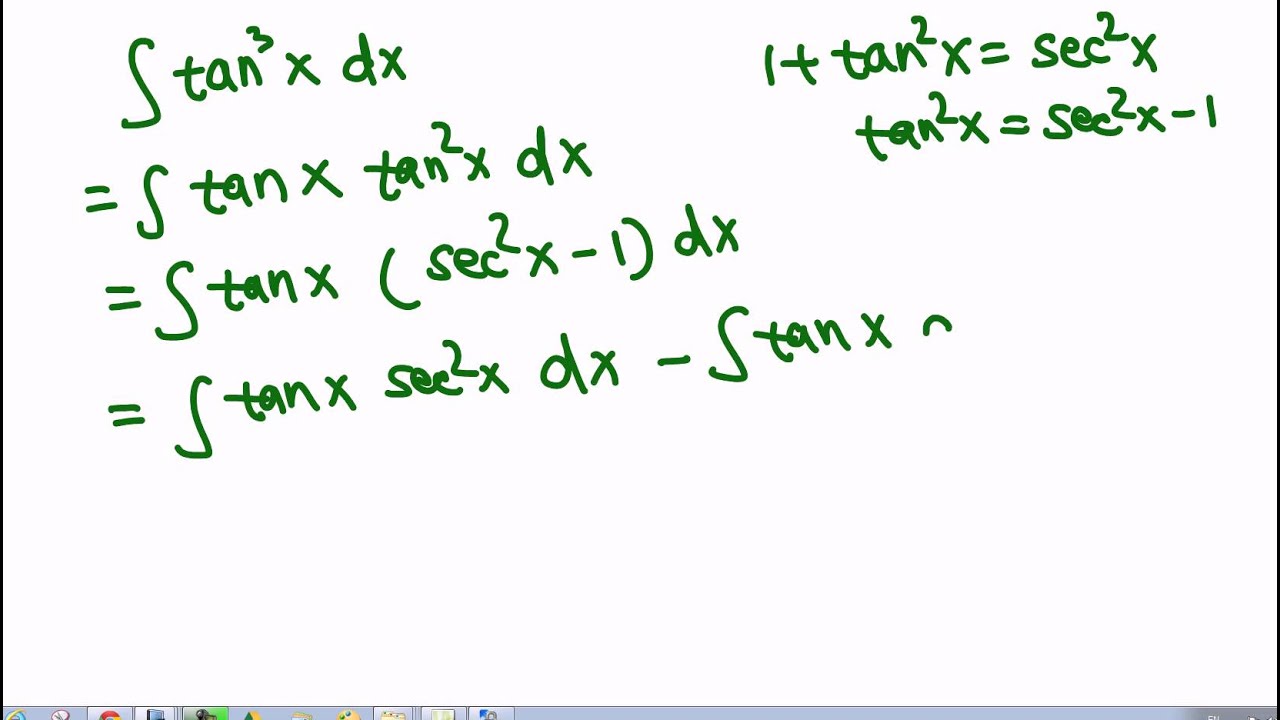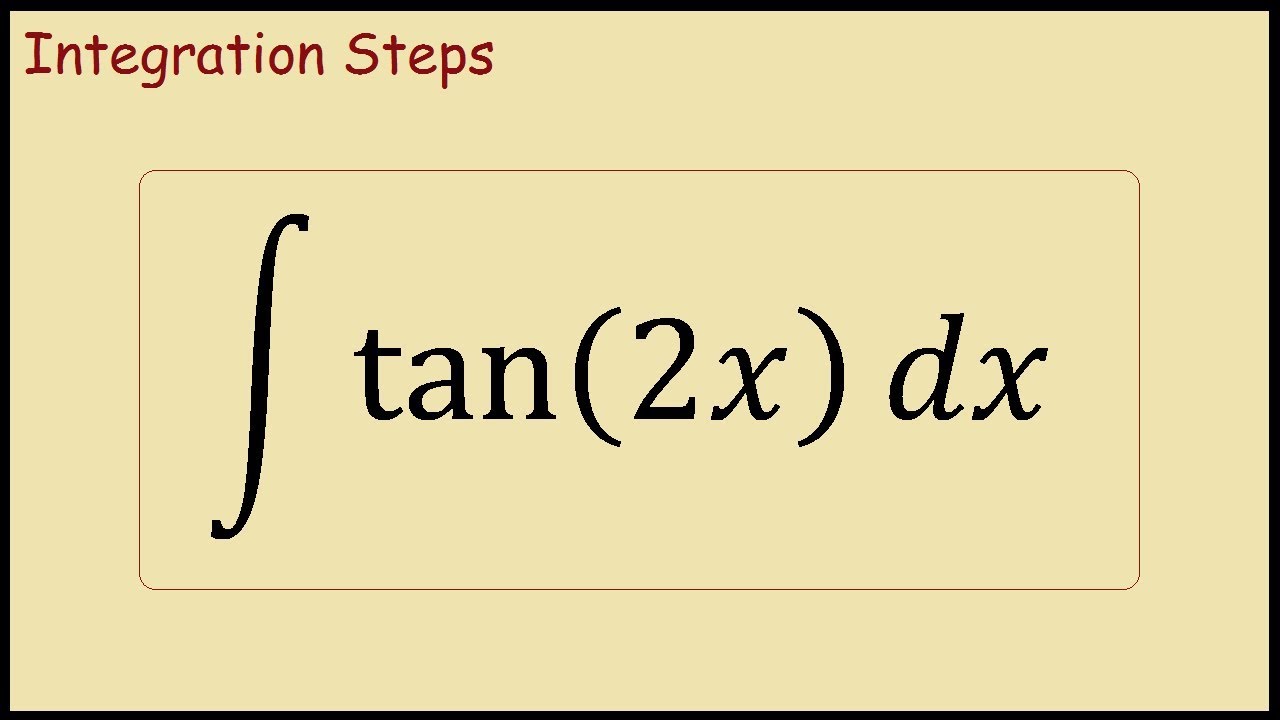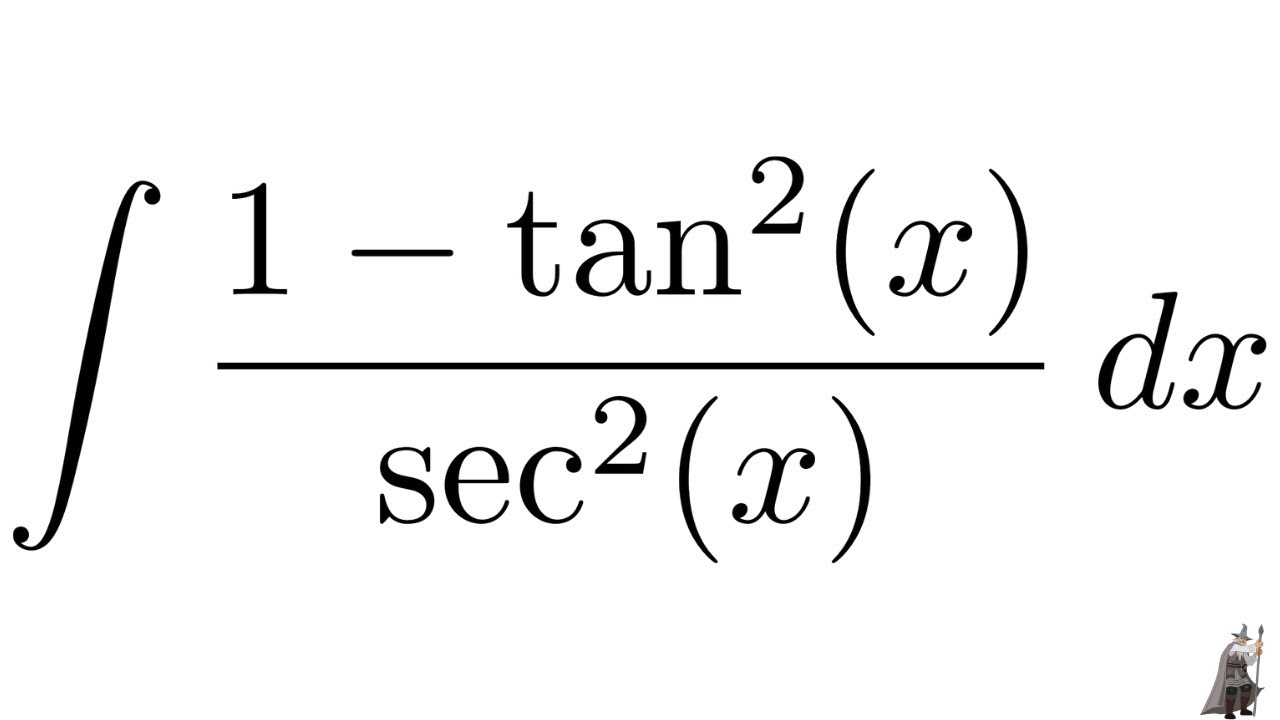Just observe that cos2xtan3x = tan3x sec2x = tan2x ⋅ tanx sec2x ⋅ 2sec2x 2sec2x = tan2x 2sec4x(2tanxsec2x) = tan2x (1 tan2x)2(tan2x) ′, thus the substitution t = tan2x gives ∫cos2xtan3xdx = ∫ t 2(1 t)2 dt Now the rest is clear Share edited Jun 3 '12 at 1656 answered Jun 3 '12 at 1646Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history Intégrale (primitive de 1/tan^2 x) Par totoro_37 dans le forum Mathématiques du supérieur Réponses 7 Dernier message , 18h15 Tan Par alixvolt dans le forum Mathématiques du collège et du lycée Réponses 3 Dernier message , 23h40 tan(x/2) = f(tan(x
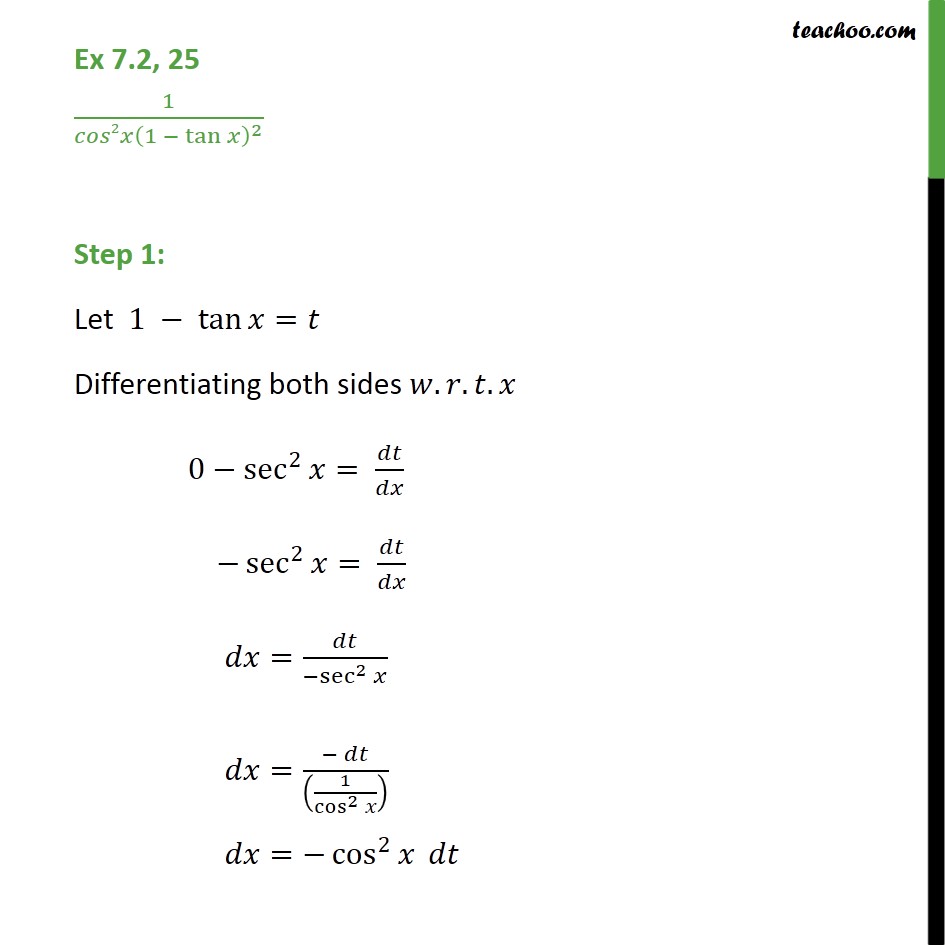
Ex 7 2 25 Integrate 1 Cos 2 X 1 Tan X 2 Ex 7 2
Integral de tan^2 x dx
Integral de tan^2 x dx- How to integrate tan^2 xFree math lessons and math homework help from basic math to algebra, geometry and beyond Students, teachers, parents, and everyone can find solutions to their math problems instantly




What Is The Integration Of Tan 2x Solution Quora
Rather, integral of (u^2)du = (u^3)/3 c In (tan^2)x your 1st mistake is not writing dx Note that dx is NOT always du!!!!! Integral of tan^2x, solution playlist page http//wwwblackpenredpencom/math/Calculushtmltrig integrals, trigonometric integrals, integral of sin(x), integIntegral of sec^2 (x) \square!
Integral udv= uvintegral vdu=logxtanx integral logxsec^2xdx so integral tanx/x dx= logxtanx integral logx sec^2xdxA now consider the second term in the rhs integal logx sec^2x dx, again applying by parts technique let u= logx , du= 1/xdx integral sec^2x dx= dv , v= tanx on integrating so this becomes logxtanx integraltanx/x dx What I get is let u = sin x then or du = cos x dx So Rather than saying u = sin x, use u = 2x instead Just expand tan u into This integral is much easier to solve Expanding sin 2x and cos 2x in terms of sin x and cos x just makes things more complicatedLet mathI = \int e^{x}tan(x) \, dx \tag1/math Using integration by parts It does not matter which of mathe^x /math and mathtan(x)/math you choose to integrate for the first integration by parts, but which you ever you choose you must
Resolvemos problemas de matemáticas respondiendo a preguntas sobre tus deberes de álgebra, geometría, trigonometría, cálculo diferencial y estadísticas con explicaciones paso a paso, como un tutor de matemáticas Hallar la integral sec(x)tan(x) Dado que la derivada de es , la integral de es Cookies y Privacidad Este sitio webThe Integral Calculator supports definite and indefinite integrals (antiderivatives) as well as integrating functions with many variables You can also check your answers!©05 BE Shapiro Page 3 This document may not be reproduced, posted or published without permission The copyright holder makes no representation about the accuracy, correctness, or



1




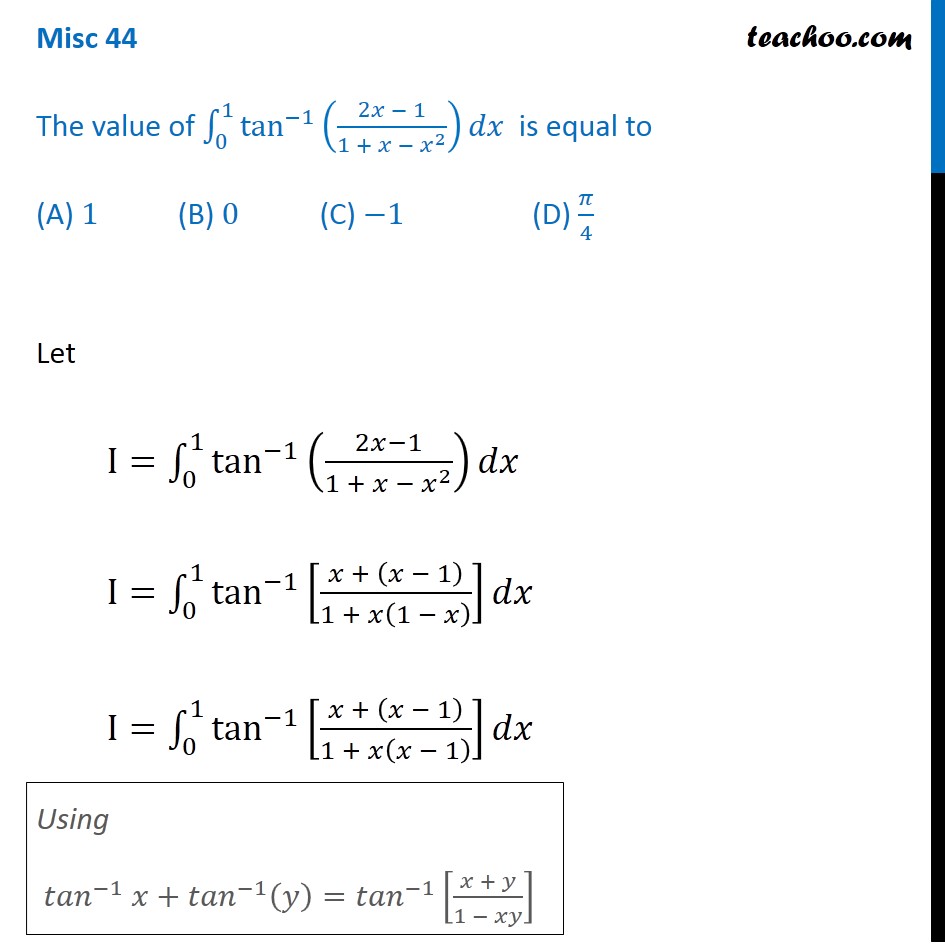
Misc 44 Value Fo Tan 1 2x 1 1 X X2 Dx Is Miscellaneous
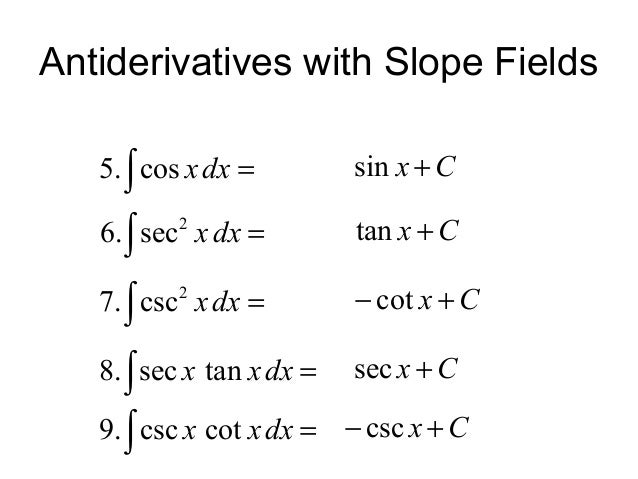
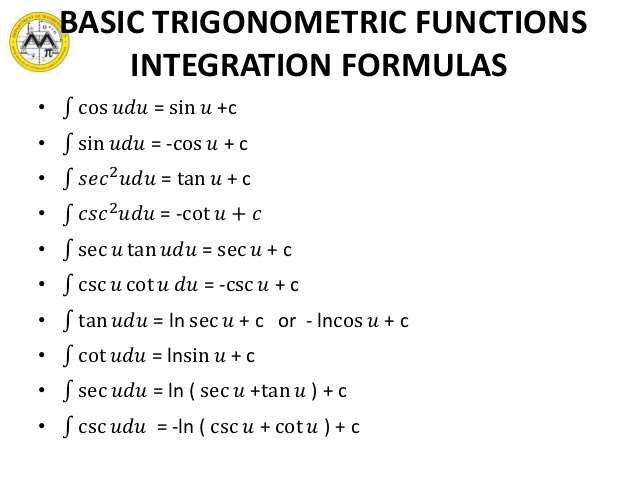
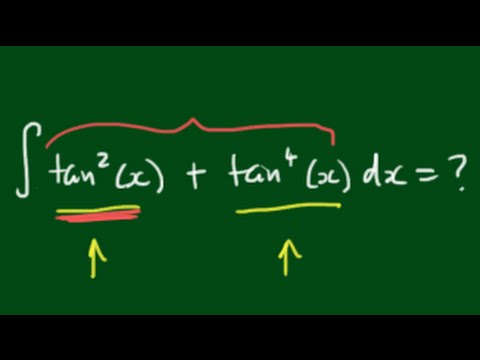
Derivadas Aplicaciones de la derivada Limites Integrales Aplicaciones de la integral Aproximación integral Series EDO Cálculo multivariable Transformada de Laplace Serie de Taylor/Maclaurin Serie deIn this video, I demonstrate how to simplify the integral ∫tan^2(x) tan^4(x)dx by factoring out tan^2(x), transforming it to ∫tan^2(x)sec^2(x)dxFrom here,Integral (1 tan^2(x))/sec^2(x)integrating powers of tangent and secant




Integrate Tan X Tan 2x Tan 3x Dx Maths Integrals Meritnation Com




Finding The Antiderivative Of 1 Cos X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
证明 cot (2x)= (1tan^2 (x))/ (2tan (x)) \square!Integral of sec^3x https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=6XlSP58uisintegral of sec(x) https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=CChsIOlNAB8integral of tan^2x*secxintegralCalculadora de Integrales Integral de tan (2*x) para x log (sec (2*x))/2 Atención log logaritmo natural Dibujar Editar expresión Enlace directo a esta página Calculadora de Integrales calcula una integral indefinida (antiderivada) de una función con respecto a una variable dada mediante la integración analítica
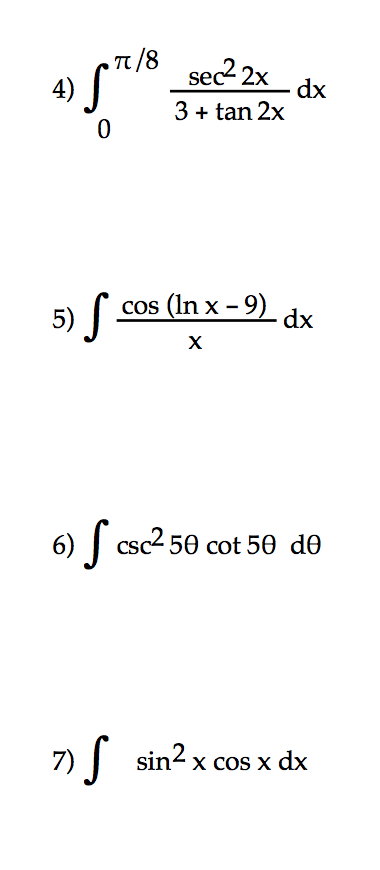



Integral Pi 8 0 Sec 2 2x 3 Tan2x Dx Integral Cos Ln Chegg Com
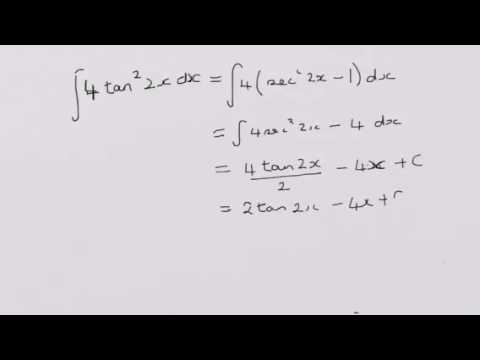



Integrating Tan 2 2x Youtube
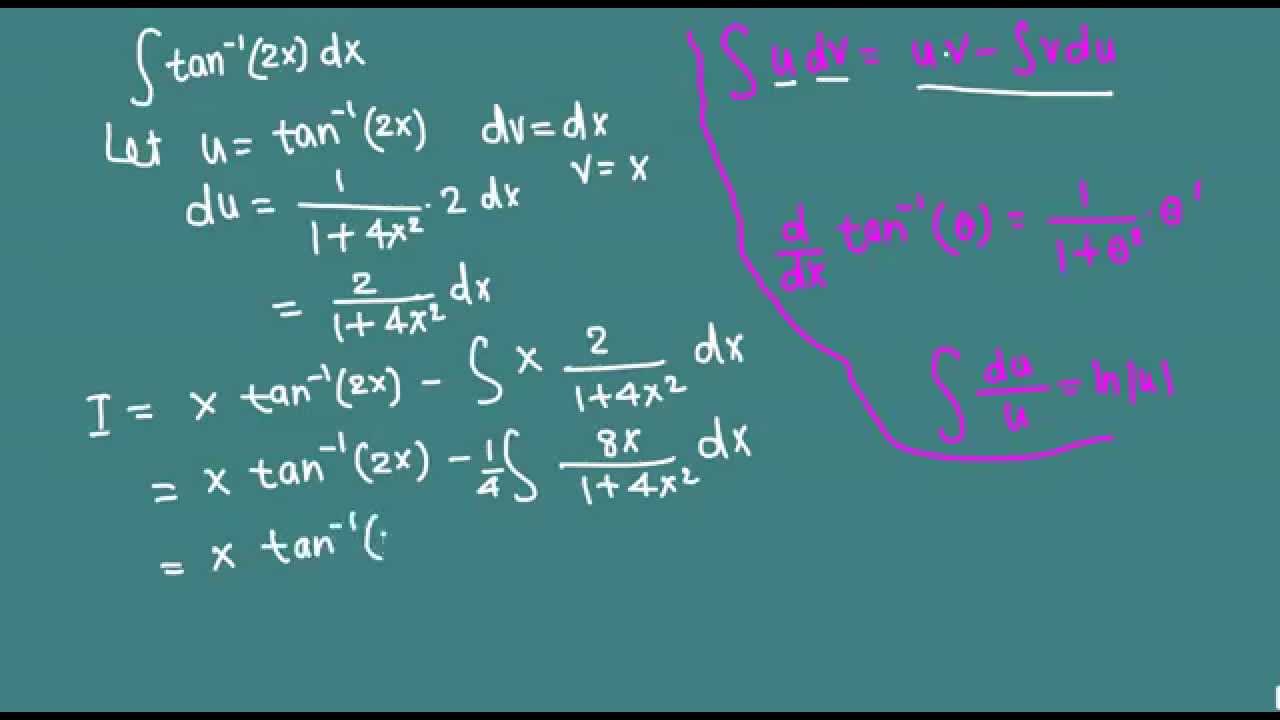
\\int \tan^{2}x \, dx\ > Integral Of Secant Cubed Wikipedia Trigonometric Integrals Geogebra Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Qué significa integral de tg x en Matemáticas Diccionario Matemáticas Cálculo Integral de tg xDerivadas Aplicações da derivada Limites Integrais Aplicações da integral Aproximação de integral Séries EDO Cálculo de Multivariáveis Transformada de Laplace Séries de Taylor/Maclaurin Série de Integral Of The Secant Function Wikipedia 2 #(1)color(red)(intf(x)^nd/(dx)(f(x))dx=f(x)^(n1)/(n1)c, where,(n!=1,f(x)>0 and f'(x)!=0)# We have, #I=inttan^2xsec^4xdx# #=int tan^2x(sec^2x)sec^2xdx# #=inttan^2x(1tan^2x)sec^2xdx# #=int tan^2xsec^2xdxinttan^4xsec^2xdx# #=int(tanx)^2d/(dx)(tanx)dxint(tanx)^4d/(dx)(tanx)dx# #=(tanx)^3/3(tanx)^5/5cto\\int \tan^{2}x\sec{x} \, dx\ > Misc 44 Value Fo Tan 1 2x 1 1 X X2 Dx Is Miscellaneous 1 Use Subtitution tan x dx = sin xIntegrate 1/(cos(x)2) from 0 to 2pi; Use tan^2 x = sec^2 x 1 first x tan^2 x = xsec^2 x x int x dx = x^2/2 int x sec^2 x dx Let u = x and dv = sec^2 x dx, so that du = dx and v = tan x to get int x sec^2 x dx = x tan x int tan x dx Now integrate tan x = sinx/cosx using substitution u = cos x int x sec^2 x dx = x tan x ( ln abs(cosx)) = x tan x ln abs cosx Finish by putting it all together int x tan^2 x = x^2/2 x tan x How Do I Integrate Tan 2 X Youtube Integration By Parts If you let u=tanx in integral (tan^2)x you get integral u^2 dx which is not (u^3)/3 c since du= sec^2x dx You must log in or register to reply hereAntiderivative of 2tan x sec x Compute tan x sec 2 x dx in two different ways a) By substituting u = tan x b) By substituting v = sec x c) Compare the two results Solution a) Compute tan x sec 2 x dx by substituting u = tan x If u = tan x 2then du = sec x dx and tan x sec 2 x dx = u du = 1 u2 c 2 = 1 tan2 xThe integral is equal to #01 The area of the region bounded by the parabola (y – 2)^2 = x – 1, the tangent to the parabola The integral is equal to #02 Integration Of Tan 3 X Youtube Why Does My Answer To The Integral Of Frac X 2 X 2 9 Need To Be Multiplied By 3 Mathematics Stack Exchange To avoid ambiguous queries, make sure to use parentheses where necessary Here are some examples illustrating how to ask for an integral integrate x/(x1) integrate x sin(x^2) integrate x sqrt(1sqrt(x)) integrate x/(x1)^3 from 0 to infinity;Int (tan (x)^2,x) integrate tan (x)^2 for x \int \tan^ {2}x \, dx 1 Usa Identidades Pitagóricas tan 2 x = sec 2 x − 1 \tan^ {2}x=\sec^ {2}x1 tan2x = sec2x− 1 ∫ sec 2 x − 1 d x \int \sec^ {2}x1 \, dx ∫ sec2 xFind the Integral tan (3x) tan (3x) tan ( 3 x) Let u = 3x u = 3 x Then du = 3dx d u = 3 d x, so 1 3du = dx 1 3 d u = d x Rewrite using u u and d d u u Tap for more steps Let u = 3 x u = 3 x Find d u d x d u d x Integral Of 1 Tan 2 X Integral Example Youtube Integral 2 \\int \tan^{2}x\sec{x} \, dx\ > 1 Integral Of The Secant Function Wikipedia Interactive graphs/plots help visualize and better understand the functions For more about how to use the Integral Calculator, go to "Help" or take a look at the examplesMath\frac{1}{\tan 2x} /math can be written as \mathcot 2x/math which can further be written as math\drac{\cos 2x}{\sin 2x}/math Here make the substitutionIntegrate x^2 sin y dx dy, x=0 to 1, y=0 to pi; Evaluate Int Tanxsec 2x 1 Tan 2x Dx What Is The Integral Of Math Sqrt Tan X Math Quora X = t , then the integral reduces to ∫ sin 3 x cos 2 x d x = ∫ − ( 1 − t 2) t 2 d t This can easily be solved Share edited May 15 '14 at 1455Cálculo Derivadas Aplicações da derivada Limites Integrais Aplicações da integral Séries EDO Cálculo de Multivariáveis Transformada de Laplace Séries de Taylor/Maclaurin Série de Fourier Funções Equações de reta Funções Aritmética e composição Seções cônicas Matrizes e vetores Matrizes Vetores GeometriaAs there is no way to immediately integrate tan^2 (x) using well known trigonometric integrals and derivatives, it seems like a good idea would be writing tan^2 (x) as sec^2 (x) 1 Now, we can recognise sec^2 (x) as the derivative of tan (x) (you can prove this using the quotient rule and the identity sin^2 (x) cos^2 (x) = 1), while we get Integral Sec2x Tan2x Dx Youtube Integral Of The Secant Function Wikipedia Dave's Math Tables Integral tan (x) ( Math Calculus Integrals Table Of tan x) Discussion of tan x = lncos x C 1 Proof Strategy Make in terms of sin's and cos's;\\int \tan^{2}x\sec{x} \, dx\ > < #I=inttan^2(x)sec(x)dx# Let #tan^2(x)=sec^2(x)1# which comes from the Pythagorean identity #I=int(sec^2(x)1)sec(x)dx=intsec^3(x)dxintsec(x)dx# The integral of #sec(x)# is well known #I=intsec^3(x)dxln(abs(sec(x)tan(x)))# The integral of #sec^3(x)# can be found through integration by parts with #u=sec(x)# and #dv=sec^2(x)dx# at this linkYou can also see how to integrate #sec(x Ex 7 2 21 Integrate Tan2 2x 3 Class 12 Cbse Ex 7 2 Lesson 7 2 Hard Trig Integrals Strategies For Integral of tan^2 (x) \square!Integrate tan (x)^3 for x \int \tan^ {3}x \, dx 1 Use Pythagorean Identities tan 2 x = sec 2 x − 1 \tan^ {2}x=\sec^ {2}x1 tan2x = sec2x− 1 ∫ ( sec 2 x − 1) tan x d x \int (\sec^ {2}x1)\tan {x} \, dx ∫ (sec2x− 1)tanxdx 2 Recall that ∫xadx = xa1 a 1 C Where C is the constant of integration Therefore, ∫udu = ∫u1du = u11 1 1 C = u2 2 C Rewrite in terms of x Since u = tanx,u2 = tan2(x) u2 2 C = tan2(x) 2 C Thus, ∫tanxsec2(x)dx = tan2(x) 2 C Answer link Integral Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Dx Integral Sec 3 X Chegg Com Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us! How Do You Integrate Int Sec 2theta Sintheta D Theta Socratic Answered Evaluate The Integrals In Exercises Bartleby What Is The Integration Of Tan 2x Solution Quora Weierstrass Substitution Wikipedia Ex 7 9 7 Direct Integrate Tan X Dx From 0 To Pi 4 Ex 7 9 What Is The Integral Of Tan 3x Quora Examples Int Tan 2x Sec 4x Dx Youtube How To Integrate X Tan 2 X Dx Quora What Is The Integral Of Cos 2x Cos Square X Evaluate The Following Integrals 3sin X 4cos X 5 Cos 2x 6 Sin 2x Tan 2x Cot 2x Dx Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community 10 4 Integration Of Powers Of Trigonometric Functions Integral Table Solving The Integral Of Cos 2x Video Lesson Transcript Study Com Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube Int Tan 2 X Dx What Is Math Int Tan 2 2x Dx Math Quora Integral Of Tan2x Integration Of Tan2x Antiderivative Of Tan2x Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube Integral Tan 4 2x Dx Chegg Com Solved Evaluate The Integral Int Sec 2 X Tan Integral Of Sec 6 X Tan 2 X Dx How Do You Integrate Sinx 2 Dx Socratic Integrate Tan 2x By Parts Integration Of Inverse Tan 2x Integration By Parts Youtube Integrate The Given Function Integrate Tan 42x Dx Chegg Com Tricks For Trigonometric Integrals M Odd Aˆ 1 Aˆ Cos U Cosx Ex 7 6 24 Integrate E X Sec X 1 Tan X Dx Is A E X Cos X Calculus Ii Trigonometric Integrals Evaluate Integral Tan X 5 Sec X 4 Dx Physics Forums Evaluating The Integral Tan 2 X Tan 4 X Dx Youtube Misc 32 Definite Integral X Tan X Sec X Tanx Miscellaneous Evaluate Each Integral A Integral 3x X 2 4 Dx Chegg Com Integral Of Tan 2 X Youtube What Is The Integral Of Tan X 6 Socratic Integration By Parts Int Tan 2 4x Sec 4x Dx Mathematics Stack Exchange 3 Integrals Tan X Sec 4 X Dx Integrals E X 2x Chegg Com Integral Of Tan 2 2x Calculus 1 Trig Integrals Youtube Powers Of Trigonometric Functions A N T I D E R I V A T I V E O F T A N 2 X Zonealarm Results Trigonometric Substitution Wikipedia Integral Of 1 Tan X Substitution Youtube How Do You Integrate 1 Tan2x Sec2x Dx Socratic Evaluate Integral Tan 3 Xdx Smallcircle Tan X Ln Chegg Com Integral Of Tan 2x Youtube Integral Tan 3 X Sec X Dx Integral Tan 2 X Sec 4 X Chegg Com Weierstrass Substitution Wikipedia Q77 Integral Of X Tan 2x Youtube Weierstrass Substitution Wikipedia Integrate Inttan 1 3x X 3 1 3x 2 Dx Integral Of The Secant Function Wikipedia Integral 2x Sec X 2 Tan X 2 Dx Integral Cot Theta D Chegg Com How Do We Integrate Math Int X Tan X Dx Math Quora Integrate Tan 2x Integration Of Tan 3 X Youtube Integral 1 0 X X 2 4x 13 Dx 1 2 Ln 18 13 Chegg Com How Do You Integrate Sin 1 X Socratic Ex 7 1 18 Integrate Sec X Sec X Tan X Dx Class 12 Integral 2 Calculo Integral How Do You Integrate Int Sec 2x 1 Tanx 3 Using Substitution Socratic Integrate X 2 Tan 1 X Dx Foreign 12 Maths Integrals Meritnation Com How Do You Integrate Sinx 2 Dx Socratic Ex 7 2 25 Integrate 1 Cos 2 X 1 Tan X 2 Ex 7 2 What Is The Integration Of Tanx Quora 1 A Evaluate The Indefinite Integral Se T Sin Chegg Com Ex 7 3 16 Integrate Tan 4 X Teachoo Maths Ex 7 3 Dtube How Do I Integrate Tan 2 X Steemit Lecture 4 Techniques For Integration Ii Part Ii Integral Of The Tanx Integral Of Secant Cubed Wikipedia The Value Of Integral I Int 0 Pi 4 Tan 2 X 2sin 2 X Integral Of Secant Cubed Wikipedia Integral Of Sec 6 X Tan 2 X Dx How Do You Find The Antiderivative Of Int Sin 2xdx Socratic What Is The Integral Of Math Sqrt Tan X Math Quora How To Integrate Tan 2x Youtube Integral 1 Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Youtube What Is The Integration Of Tan 2x Solution Quora